What is IIoT/Industry 4.0?
Introduction
Industry 4.0 refers to the transformation of industry through the intelligent networking of machines and processes with the help of information and communication technology.
● The term is used interchangeably with the ‘fourth industrial revolution.
● Industry 4.0 comes from the German term ‘Industry 4.0’ It was first used in a project in the high-tech strategy to transform German manufacturing in which the Internet of Things and cyber-physical systems took center stage, along with a further focus on production, people, environment, and security.
● It is the digital transformation of production and related industries and value creation processes. Products and means of production get networked and can communicate, enabling new ways of production, value creation, and real-time optimization.
● Cyber-physical systems create the capabilities needed for smart factories. These are the same capabilities we know from the Industrial Internet of Things like remote monitoring or track and trace.
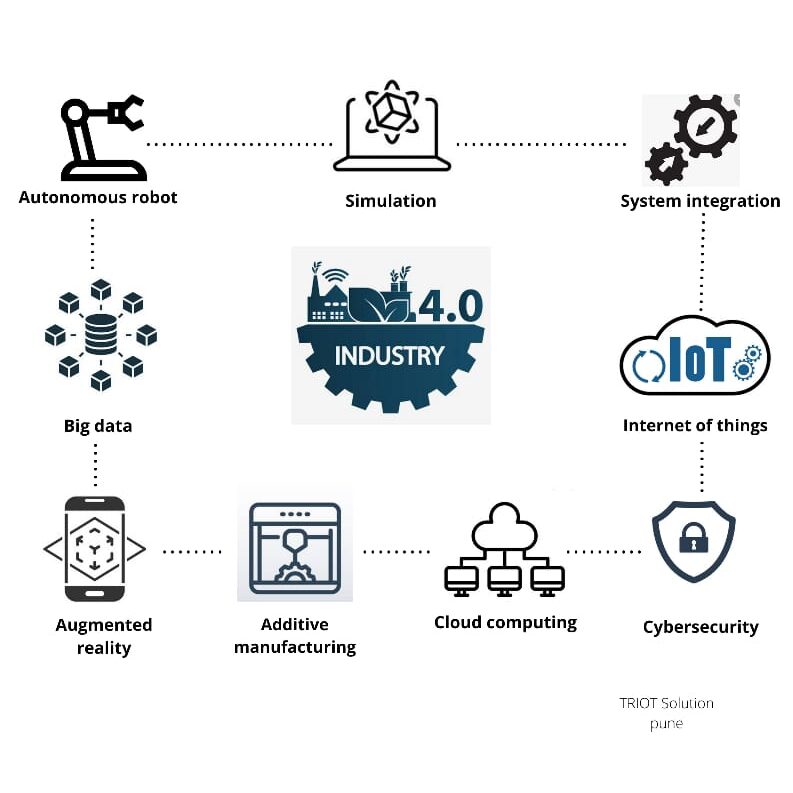
1. Big data
In Industry 4.0, Big Data is collected from a wide range of sources, from factory equipment and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, to ERP and CRM systems, to weather and traffic apps.
2. Cloud computing
It provides the foundation for most advanced technologies from AI and machine learning to
the Internet of Things and gives businesses the means to innovate.
3. Augmented reality
Augmented reality, which overlays digital content on a real environment, is a core concept of
Industry 4.0. With an AR system, employees use smart glasses or mobile devices to visualize
real-time IoT data, digitized parts, repair or assembly instructions, training content, and more
when looking at a physical thing like a piece of equipment or a product.
4. IOT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical objects that contain embedded
technology to communicate and sense or interact with their internal states or the external
environment. Most physical things in Industry 4.0 devices, robots, machinery, equipment,
products use sensors and RFID tags to provide real-time data about their condition,
performance, or location.
5. Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is another key technology driving Industry 4.0, 3D
printing was initially used to as a rapid prototyping tool but now offers a broader range of
applications, from mass customization to distributed manufacturing.
6. Autonomous robots
With Industry 4.0, a new generation of autonomous robots is emerging. Programmed to
perform tasks with minimal human intervention, autonomous robots vary greatly in size and
function, from inventory scanning drones to autonomous mobile robots for pick and place
operations. Equipped with cutting edge software, AI, sensors, and machine vision, these
robots are capable of performing difficult and delicate tasks and can recognize, analyze, and
act on information they receive from their surroundings.
7. Simulation
Simulation is the term for developing planning exploratory models to optimize decision
making as well as the design and operations of complex and smart production system.
8. Cybersecurity
With the increased connectivity and use of Big Data in Industry 4.0, effective cybersecurity is
paramount. By implementing a Zero Trust architecture and technologies like machine
learning and blockchain, companies can automate threat detection, prevention, and response –
and minimize the risk of data breaches and production delays across their networks.
Major component of Industry 4.0 :
- CPS (Cyber physical system:
- IOT (Internet of things)
- Cloud computing
- Cognitive computing
- CPS (Cyber-physical system)
Cyber-physical system the term at integrating cyber and physical manufacturing process,
either in other words computer and network should monitoring the physical manufacturing
processes at the different level. - IOT (Internet of things)
IOT is the term to enable Machineries & objects like sensor & mobile phones to
communicate while allowing human to all workout solutions. Such integration makes it easy
for cyber physical system to work and solve problem at independent level. The internet of
things is the support system of cyber physical system cooperation with each other via unique
address scheme.
- Cloud computing
Cloud computing is the term refers to any kind of hosted service delivered over the
internet. These services including servers, software, networks, databases, analytics and other
computing function can be operated through the cloud. - Cognitive computing
Cognitive computing is the term which is emerging typical cases of intelligent computing
methodologies and systems that implements computational intelligence by autonomous
inferences and perceptions mimicking the mechanisms of the brain.
Benefits of IIoT/Industry 4.0
- Productivity. In simple terms, Industry 4.0 technologies enable you to do more
with less. - Improved Efficiency.
- Increased Knowledge Sharing and Collaborative Working.
- Flexibility and Agility.
- Makes Compliance Easier.
- Better Customer Experience.
- Reduces Costs.
- Creates Innovation Opportunities.
Application Of Industry 4.0
Main objective of industry 4.0 is to increase the automation so as contribute to the
operational efficiency and effectiveneeso0f the company. Industry 4.0 based on the
integration of new technical solutions.
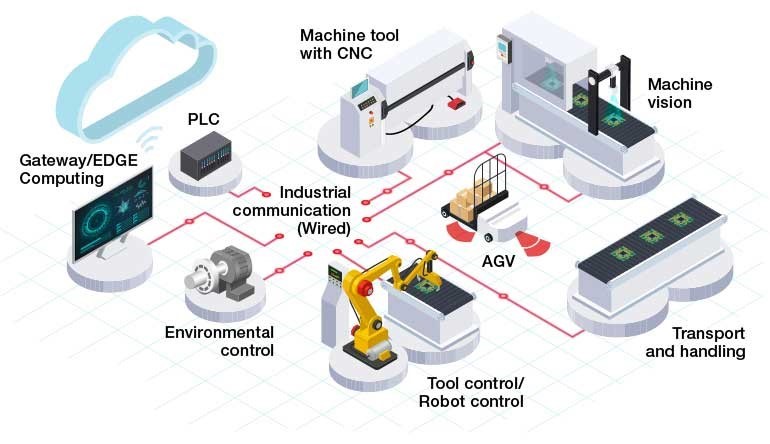
Industrial application can be of different types, such as process control manufacturing
automation, and energy management and application.
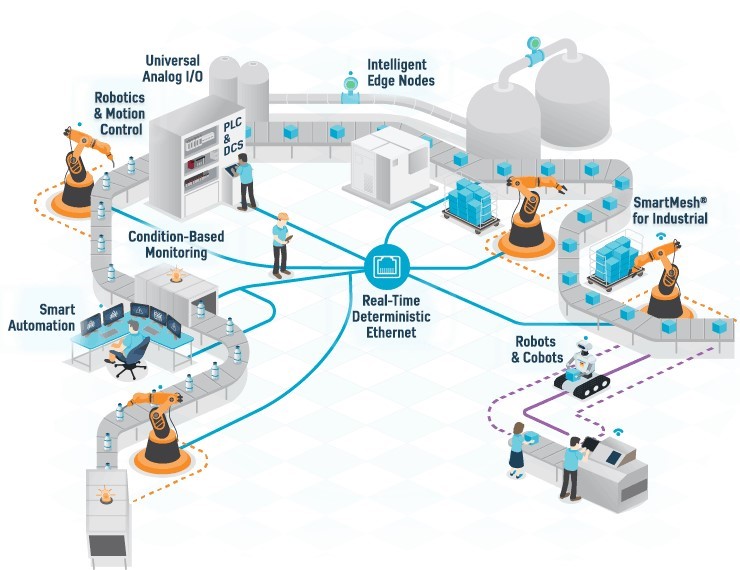
FACTS
Industry 4.0 fosters what has been called a “smart factory”. Within modular
structured smart factories, cyber-physical systems monitor physical processes, create a
virtual copy of the physical world and make decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of
Things, cyber-physical systems communicate and cooperate with each other and with
humans in real-time both internally and across organizational services offered and used by
participants of the value chain.
Smart manufacturing is a broad category of manufacturing that employs
computer-integrated manufacturing, high levels of adaptability and rapid design changes,
digital information technology, and more flexible technical workforce training. Other
goals sometimes include fast changes in production levels based on demand, optimization
of the supply chain, efficient production and recyclability. In this concept, as smart
factory has interoperable systems, multi-scale dynamic modelling and simulation,
intelligent automation, strong cyber security, and networked sensors.
Big data processing Smart manufacturing utilizes big data analytics, to refine complicated
processes and manage supply chains. Big data analytics refers to a method for gathering
and understanding large data sets. The definition of smart manufacturing covers many
different technologies. Some of the key technologies in the smart manufacturing
movement include big data processing capabilities, industrial connectivity devices and
services, and advanced robotics.
Challenges
Now that we speak about competitive benefits and customization, we also need to tackle
agility, scalability and flexibility. The same scalability and agility which we expect from
supporting IT services and technologies, such as the cloud are expected in manufacturing.
This is partially related with the previous topic of customization but mainly is about
leveraging technologies, Big Data, AI, robots and cyber-physical systems to predict and
meet seasonal demand, fluctuations in production, the possibility to downscale or upscale;
in other words: all the adjustments that are sometimes more or less predictable, can be
made more predictable or are not predictable but can be handled thanks to increased
visibility, flexibility and a possibility to leverage assets in function of optimal production
requirements from a perspective of time and scale. The development of innovative
capabilities and new revenue models. Digital transformation, as you can read in our
digital transformation strategy overview, is a matter of many levels, steps and capabilities.
You can transform processes, specific functions, customer service, experiences and
skillsets but in the end true value is generated by tapping into new, often information intensive, revenue sources and ecosystems, enabling innovative capabilities, for instance
in deploying an asa service capacity for customers, advanced maintenance services and so
on.
Conclusion :
In Industry 4.0, more than ever before, it is the key to success. Germany is well placed to
take a leading role in the provision and implementation of Industry 4.0 solutions. The
central government and federal states have launched strategic initiatives to drive its
development. Initiate all sector to need implement the industry 4.0 to making the
simplicity, and improve the productivity.